Raynaud's Disease is a vasospastic disorder most commonly affecting the hands and feet. A vasospasm occurs when the smooth muscles controlling the small arteries supplying circulation into the hands and feet contract. This smooth muscle contraction, or spasm, makes the arteries so small that blood has difficulty passing through. The most common event causing the vasospasm is exposure to cold temperature. Raynaud's disease must be differentiated from Raynaud's phenomenon. Raynaud's disease is a disease that is not associated with any other specific disease entity. Raynaud's phenomenon has the same findings, as Raynaud's disease except there is an underlying disease associated with the vasospasm. Raynaud's phenomenon may be seen with rheumatoid arthritis, scleroderma, lupus, and other diseases. The condition is aggravated by smoking. A single cigarette may decrease the circulation by one half for more than an hour. Raynaud's disease is most common in young women, and has no known cause. It typically is found in both feet and both hands. It appears that the threshold for vasospasm is lowered in these individuals, and may occur following exposure to cold, or during times of stress.
Diagnosis
The diagnosis of Raynaud's disease is a clinical diagnosis based upon the patients' symptoms and the findings on examination. Patients with Raynaud's disease will often hear the expression, ""Cold hands, warm heart"" when shaking hands with others. This is because the arterial vasospasm decreases blood flow into the hands and feet. In addition to the cold skin temperature, there is a pattern of color changes seen in the fingers and toes. Initially after exposure to cold, the toes and fingers will turn white, then as the oxygen is depleted they become cyanotic which is a blue color, finally the spasm relaxes and there is an excess of blood flow which turns the toes red and warm (reactive hyperemia). This pattern of triphasic color change, white to blue to red, is a hallmark of Raynaud's disease. However, not all individuals will have the triphasic (three-color) change. Some will have a biphasic (two color) change going directly from white to red.
The length of vasospasm may last from several minutes to several hours. This may be accompanied by pain, or more commonly by numbness. In severe cases there may damage to the skin on the tips of the toes and fingers with an appearance similar to frostbite. These areas may develop into ulcers (sores) which can be very painful.
Treatment
In mild forms of Raynaud's disease the simplest treatment is to protect the hands, and feet from cold exposure. Since cold is the cause of the vasospasm, preventing exposure to cold will prevent the spasm from occurring. This may require insulated boots and thick warm socks in colder climates. Dressing in layers, with new polyester liners and new insulating materials may be helpful. Most sporting goods stores that stock hiking or camping equipment will be able to help in this regard. Cigarette smoking contains nicotine, which is known to cause vasospasm. Discontinuation of cigarette smoking will be a definite benefit for the individual with Raynaud's disease. In more severe cases, or in those with recurrent episodes, medications are available to help relax the arterial smooth muscle. Medications that have been used successfully in some individuals include phenoxybenzamine, prazosin, nifidipine, pentoxyphylline, and guanethidine. These medications are only available by prescription, and patients must be monitored for potential side effects.
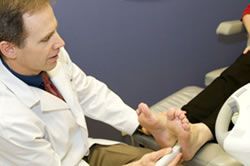 Diagnostic ultrasound imaging has greatly improved the services and diagnostic options available to our patients. For example, those soft tissue problems that otherwise cannot be seen on x-rays can often be seen with ultrasound imaging. Tendon problems and the plantar fascia itself can be clearly visualized and evaluated. Often this can be done right during office visit rather than setting up a much more costly MRI. Foreign bodies such as glass and metal objects can be identified and mapped out. Soft tissue growths such as a ganglion cyst show up very clearly with ultrasound imaging.
Diagnostic ultrasound imaging has greatly improved the services and diagnostic options available to our patients. For example, those soft tissue problems that otherwise cannot be seen on x-rays can often be seen with ultrasound imaging. Tendon problems and the plantar fascia itself can be clearly visualized and evaluated. Often this can be done right during office visit rather than setting up a much more costly MRI. Foreign bodies such as glass and metal objects can be identified and mapped out. Soft tissue growths such as a ganglion cyst show up very clearly with ultrasound imaging.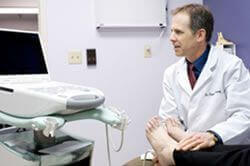 spur injections and injections for plantar fasciitis with cortisone are much more effective when they are placed directly in the most inflamed portion of the plantar fascia. Another example is ultrasound guided injections for Morton's neuroma. Dehydrated alcohol is utilized for sclerosis of the pathologic nerve tissue. This is done instead of typical neuroma surgery.
spur injections and injections for plantar fasciitis with cortisone are much more effective when they are placed directly in the most inflamed portion of the plantar fascia. Another example is ultrasound guided injections for Morton's neuroma. Dehydrated alcohol is utilized for sclerosis of the pathologic nerve tissue. This is done instead of typical neuroma surgery.






 We have x-ray equipment within our clinic that includes the x-ray unit and the automatic x-ray film processor. This allows us to take any ankle and foot x-rays needed. X-ray films are quickly developed by the automatic processor, so they are available if necessary during the same office visit.
We have x-ray equipment within our clinic that includes the x-ray unit and the automatic x-ray film processor. This allows us to take any ankle and foot x-rays needed. X-ray films are quickly developed by the automatic processor, so they are available if necessary during the same office visit.
