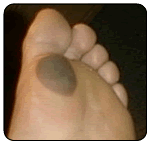
Malignant Melanoma
Pigmented lesions should always be inspected and observed. Most pigmented areas are nothing but freckles and moles. However a potentially deadly pigmented lesion that can occur on the foot and lower extremity is Malignant Melanoma. A physician should evaluate any pigmented lesion that suddenly occurs or a pigmented lesion that starts to change its appearance. These changes are usually subtle and may consist of increased size and depth of color, onset of bleeding, seepage of clear fluid, tumor formation, ulceration and formation of satellite pigmented lesions. The color is usually not uniform but is likely to be scattered irregularity, being brown, bluish black or black. An increase in pigmentation may precede enlargement of the lesion by several months. Although any part of the body may be affected, the most frequent site is the foot, then in order of frequency, the remainder of the lower extremity, head and neck, abdomen, arms and back. Malignant melanoma may also form under the nails of the feet and hands. The thumb and big toe are more commonly affected than the other nails. Quite often the adjacent skin to the nail is ulcerated. Usually a fungal infection is suspected and antifungal treatment may be administered for months before the true nature of the lesion is discovered. A black malignant melanoma of the toe can also be mistaken for gangrene. Overall, the incidence of malignant melanoma is quite low.
Actinic Keratosis
Another cancer causing lesion that can occur on the feet are called Actinic Keratosis. Although most commonly found in sun-exposed areas of the body such as the face, ears, and back of the hands, these lesion can also occur on the foot. They are characterized as either flat or elevated with a scaly surface. They can either be reddish or skin colored. On the foot they are frequently mistaken for plantars warts. These lesions are the precursor of epidermoid carcinoma. Treatment for these lesions should be through as they are definitely precancerious. Treatment consists of freezing the lesions with liquid nitrogen or sharp excision.
Kaposi's Sarcoma
Yet another cancerous lesion that can occur on the foot is called Kaposi's Sarcoma. These lesions occur most commonly on the soles of the feet They are irregular in shape and have a purplish, reddish or bluish black appearance. They tend to spread and form large plaques or become nodular. The nodular lesions have a firm rubbery appearance. The appearance of these lesions is an ominous sign. In the late 1970's and early 1980's an outbreak of Kaposi's sarcoma occurred in San Francisco, California. It was later learned that the disease was associated with AIDS infection. It can occur without the concurrent AIDS infection but this is very rare.
Chronic athlete's foot can cause an increased pigmentation to the bottom of the foot. It is associated with dry scaling skin and may have a reddish appearance.
Venous Stasis
Generalized increased pigmentation occurs for a variety of other reasons. Dark patches of skin occur about the ankles and lower legs in persons who suffer from Venous Stasis. Venous stasis is caused by an accumulation of fluid in the lower extremities. This is due to poor venous return of blood to the heart. Venous blood flow back to the heart occurs by way of the veins in the feet and legs. Venous stasis is associated with varicose veins that do a poor job of returning blood to the heart. As a result the blood flow is slowed, becomes stagnant, and fluid accumulates in the ankles and lower legs. As the fluid accumulates in the lower legs, the small and medium-sized veins break or leak fluid into the tissues. As blood cells break up in the tissue, they deposit the iron that is part of hemoglobin in the blood cell. The iron stains the skin causing a light to dark brownish appearance. With time, the skin and subcutaneous fat becomes thinned and will break down creating weepingvenous stasis ulcerations. At times, blistering will form with a clear, watery fluid weeping from the skin. This condition requires professional attention by a physician.
Diabetic Dermopathy
Another cause of generalized increased pigmentation is diabetes. The condition termedDiabetic Dermopathy occurs most frequently on the shins and lower legs. They may have the appearance of small scars. Their appearance may precede the diagnosis of diabetes by several years. The actual cause of diabetic dermopathy is not well understood, but it does not cause any particular problem or pose any particular health threat.
Small, spider-like areas of increased pigmentation on the ankles are caused by the break down of small veins in the area and are called Spider Veins; they also pose no health risks.






 Blisters form as a result of heat, moisture and friction. Blisters can also form as a result of fungal infections of the skin, allergic reactions or burns. If a patient has diabetes, they should be evaluated by a doctor in a timely fashion. Generally, a person will recognize a burn by association with a specific painful event. People with diabetes may not be able recognize the painful event due to a condition called neuropathy. A doctor should attend to burns. Blisters are due to fungal infection of the skin or to allergic reactions, which will generally occur in clusters and be smaller than blisters caused by friction. They will also often occur in areas of the foot, which are free from friction forces.
Blisters form as a result of heat, moisture and friction. Blisters can also form as a result of fungal infections of the skin, allergic reactions or burns. If a patient has diabetes, they should be evaluated by a doctor in a timely fashion. Generally, a person will recognize a burn by association with a specific painful event. People with diabetes may not be able recognize the painful event due to a condition called neuropathy. A doctor should attend to burns. Blisters are due to fungal infection of the skin or to allergic reactions, which will generally occur in clusters and be smaller than blisters caused by friction. They will also often occur in areas of the foot, which are free from friction forces.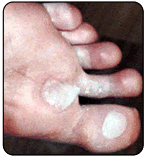 Blisters should be drained leaving the cover of the blister in tact. The area should be protected with a non-stick bandage with mild compression. Ice to "hot spots" can be soothing and reduce the thermal damage to the surrounding area. "Double socking" can prevent blisters associated with athletics. Wearing two pair of socks allows the friction to be absorbed between the socks reducing friction to the skin. A sock has been developed that helps to reduce friction and blistering called the Thro-lo sock. It is useful for athletics and for diabetic patients. They are widely available in athletic shoe and apparel stores. Skin protectant sprays and adhesive gel pads are also available.
Blisters should be drained leaving the cover of the blister in tact. The area should be protected with a non-stick bandage with mild compression. Ice to "hot spots" can be soothing and reduce the thermal damage to the surrounding area. "Double socking" can prevent blisters associated with athletics. Wearing two pair of socks allows the friction to be absorbed between the socks reducing friction to the skin. A sock has been developed that helps to reduce friction and blistering called the Thro-lo sock. It is useful for athletics and for diabetic patients. They are widely available in athletic shoe and apparel stores. Skin protectant sprays and adhesive gel pads are also available.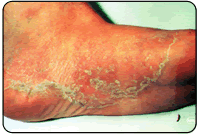 Athlete's foot is caused by a fungal infection of the skin on the foot. The majority of these infections are caused by one of three fungal agents called dermatophytes. Athlete's foot is by far the most common fungal infection of the skin. The infection can be either acute or chronic. The recurrent form of the disease is often associated with fungal-infected toenails. The acute form of the infection most often presents with moist, scaling between the toes with occasional small blisters and/or fissures. As the blistering breaks, the infection spreads and can involve large areas of the skin on the foot. The burning and itching that accompany the blisters may cause great discomfort that can be relieved by opening and draining the blisters or applying cool water compresses. The infection can also occur as isolated circular lesions on the bottom or top of the foot. As the skin breaks down from the fungal infection, a secondary bacterial infection can ensue.
Athlete's foot is caused by a fungal infection of the skin on the foot. The majority of these infections are caused by one of three fungal agents called dermatophytes. Athlete's foot is by far the most common fungal infection of the skin. The infection can be either acute or chronic. The recurrent form of the disease is often associated with fungal-infected toenails. The acute form of the infection most often presents with moist, scaling between the toes with occasional small blisters and/or fissures. As the blistering breaks, the infection spreads and can involve large areas of the skin on the foot. The burning and itching that accompany the blisters may cause great discomfort that can be relieved by opening and draining the blisters or applying cool water compresses. The infection can also occur as isolated circular lesions on the bottom or top of the foot. As the skin breaks down from the fungal infection, a secondary bacterial infection can ensue.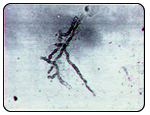 The diagnosis of tenia pedis is generally made based upon the clinical presentation. A definitive diagnosis is made by taking a scraping of the skin and culturing it. It may take up to three weeks for the culture to grow the fungus. In some instances the culture may present a false negative result because the skin scraping was inadequate. Some doctors may perform a KOH prep of a skin scraping. This is examined under a microscope and may reveal elements that can make the diagnosis.
The diagnosis of tenia pedis is generally made based upon the clinical presentation. A definitive diagnosis is made by taking a scraping of the skin and culturing it. It may take up to three weeks for the culture to grow the fungus. In some instances the culture may present a false negative result because the skin scraping was inadequate. Some doctors may perform a KOH prep of a skin scraping. This is examined under a microscope and may reveal elements that can make the diagnosis.
